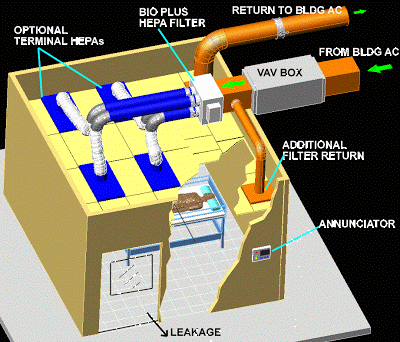
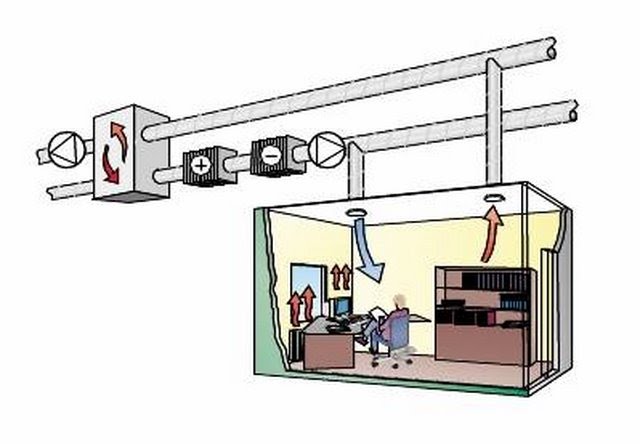
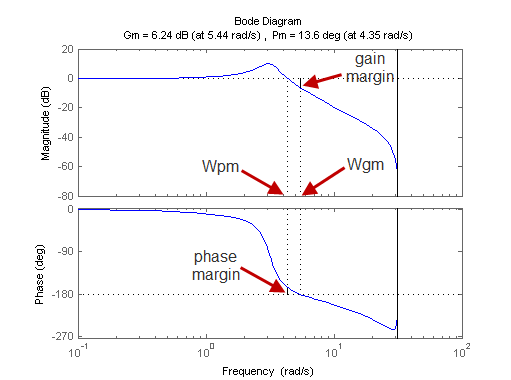
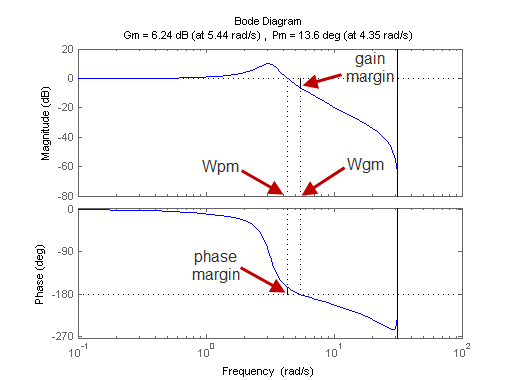
Variable Air Volume HVAC Systems
08/31/17
“How can we make a more optimal HVAC system?”
While Constant Air Volume HVAC Systems are affordable, they are not the most optimal solution. They don’t have the most precise temperature control, their fans can be noisy, and they can consume a large amount of energy. So how can we use our engineering mindset to solve this problem? Well, what if we were to have our air temperature be constant instead of our air supply? This would allow us to change the air temperature at a specified rate, allowing us to save money, energy, noise, and wear. This system is known as a Variable Air Volume HVAC System and is used in building systems all over the world.